Introduction to the Internet and the WWW.
I get the material "Introduction to the Internet and the WWW" when studying in UTeM, subjects Web App (LEC), Code 3 BITM, S1G1 Group, Lecture: PN Norazlin. You can see complete the following materials Introduction Internet and www. If you wanted to know my first day at the UTeM campuss. CLICK HERE
Internet (short for interconnection-networking) is an entire network of computers connected together using a standard global system, while the World Wide Web (www) is an information space that is used by global identifiers called Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) to identify sources useful power. WWW is often considered synonymous with the Internet as a whole, even though he is only a part thereof.
This material I got when studying in UTeM: Web App (LEC), 3 BITM, S1G1, - PN Norazlin, FTMK BK6
Internet (short for interconnection-networking) is an entire network of computers connected together using a standard global system, while the World Wide Web (www) is an information space that is used by global identifiers called Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) to identify sources useful power. WWW is often considered synonymous with the Internet as a whole, even though he is only a part thereof.
This material I got when studying in UTeM: Web App (LEC), 3 BITM, S1G1, - PN Norazlin, FTMK BK6
History of the Internet
J.C.R. Licklider
- envisioned "Galactic Network" concept - a globally interconnected set of computers through which everyone could quickly access data and programs from any site (MIT, Aug 1962)
- 1st head of the computer research program at DARPA (Oct 1962)
Lawrence G. Roberts
- develop the computer network concept & publish ARPANET (DARPA, 1967)
- ARPANET had been turned over to the Defense Communications Agency
Ira Fuchs and Greydon Freeman (1981)
- Devised BITNET, which linked academic mainframe computers for electronic mail
CSNET- 1981
- National Science Foundation (NSF) developed the Computer Science Network (CSNET) (1981) to extend the ARPANET networking benefits for computer science departments at academic & research institutions.
- The Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) was standardized, and consequently, the concept of a world-wide network of interconnected TCP/IP networks, called the Internet, was introduced. (1982)
- Commercial Internet service providers(ISPs) began to emerge in the late 1980s and early 1990s.
How does the internet work?
- What is the internet?
- A huge collection of computers connected by TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) in a network
- IP addresses
Set of four integers uniquely identifying each nodeExample: 128.135.197.76
- Since numbers are difficult to remember, the Internet evolved DNS addresses
Internet Protocol (IP)
- Computers are identified by unique numeric addresses
- Form: 32-bit binary number
- Example : 191.57.126.0 to 191.57.126.255 has 256 IP addresses
- Written as four 8-bit numbers, separated by periods
- Organizations are assigned groups of IPs for their computers
Domain Name System (DNS)
DNS translates domain names to network addresses. For example: altavista.com is 192.136.112.39
Separate domain administrations:
- Defined types: COM, EDU, GOV, BIZ, TEL, NET, ORG, INFO, NAME, MOBI
- Countries: US, JP, FR, MY, RU, CH, UK, etc.
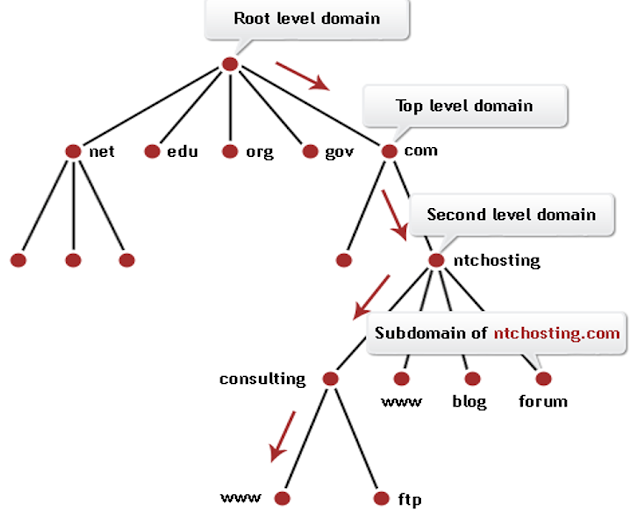
- Tree structured directory
- A DNS address (ftmk.utem.edu.my) consists of:
- Domain name for organizations (ftmk.utem.edu.my)
- institutional site name (ftmk.utem)
- top-level domain(tld) name (edu.my)
- host name for individual machines (ftmk)
 |
| Domain |
Domain naming rules:
- Max 255 characters per name
- From 2 to 5 labels per domain name
- faizal.uhost.co.tv has 4 labels
- Labels of up to 63 characters
- Allowable characters are A-Z, 0-9, and ‘-’
- Domain names are not case sensitive
- Other parts of a URL may be case sensitive
- Trademark owners get preference
World Wide Web (Web)
- Web allows computer users to locate and view multimedia-based documents on almost any subject over the Internet
- Web is an application to share and access Web documents on top of the Internet. Other applications: email, FTP, newsgroups, instant messaging, etc.
- Founded by Tim Berners Lee of CERN, 1989
- The WWW is not the Internet
- Tim developed a technology for sharing information via hyperlinked text documents called HTML
- Tim also wrote communication protocols to form the backbone of the WWW. He wrote the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) – a communication protocol used to send information over the Web
- Web documents (Web pages) are formatted in HyperText Markup Language(HTML)
Web browsers
- Client software that allows users to access the Web’s rich content
- Microsoft’s Internet Explorer, Mozilla’s Firefox, Apple’s Safari & Opera Software’s Opera
- People use web browsers to access the information available on the Web & to share or exchange the content with other users
- May include tools for e-mail, address book, news, Web authoring, etc.
- May run programs in Java, Javascript, ActiveX, or Shockwave
- Records data in Cookies, logs, cache
Web Servers
- A specialized software that responds to client requests (typically from a web browser) by providing resources such as HTML documents.
- E.g. Apache HTTP Server, Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) etc.
- Provides access to files
- Runs programs in CGI, Perl, Java, C, etc.
- May support relational database (Oracle, DB2, SQL Server, etc.)
- May provide access to legacy applications
- May log access requests
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
- All Web pages are addressed with URLs
- Format: protocol:address
- protocol may be
- ftp, http, mailto, telnet, etc
- address specifies
- A server name
- A directory path (optional)
- A filename
- Example:
http://www.eftmk.utem.edu.my/bitm2113/rajah1.png
MIME
- MIME stands for Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME)
- Originally developed for email
- Used to specify to the browser the form of a file returned by the server (attached by the server to the beginning of the document)
- Form: type/subtype
- Examples: text/plain, text/html, image/gif, image/jpeg
- Server gets type from the requested file name’s suffix: *.html implies text/html
- Browser gets the type explicitly from the server
- Experimental types
- Subtype begins with x-, example: video/x-msvideo
- Experimental subtypes are added to MIME specification stored in user’s Web server.
- Experimental types require the server to send a helper application or plug-in so the browser can deal with the file.
HTTP - Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
- Transactions between client and server
- Client connects
- Client makes one or more Requests
- Server Responds to Requests
- Client drops connection
- Http client request has three parts:
1) Method, document URL, HTTP version
Most frequently used methods are:
- GET request a document or data
- HEAD request document attributes only
- POST send data to server
2) Browser type, OS, and acceptable media
3) Optional data
5 komentar
Good Information.. :)
Thankyou Natalia :)
hmm good story bro
:)
x-) Yes. thankyou Ferry :)
It gives me a lot of information..
EmoticonEmoticon